Installing Docker Desktop
First, we are going to install Docker Desktop. Click here to get to the download page.
If this is your stance, you probably already have an alternative container runtime installed on your machine - Podman, Docker daemon, Orbstack, etc.
While these alternatives should work, there might be unforeseen consequences - let me know if you run into troubles and I'll try to help.
You may also open an issue on this site's GitHub project describing your problem.
Configuring Docker Desktop
As Educates will configure a KinD cluster according to our needs, there's a few things we need to adjust in Docker Desktop, the underlying runtime:
Open Docker Desktop, navigate to the Settings page by clicking the :octicons-gear-16: icon in the top-right corner, and make sure the [Advanced] settings look like this.
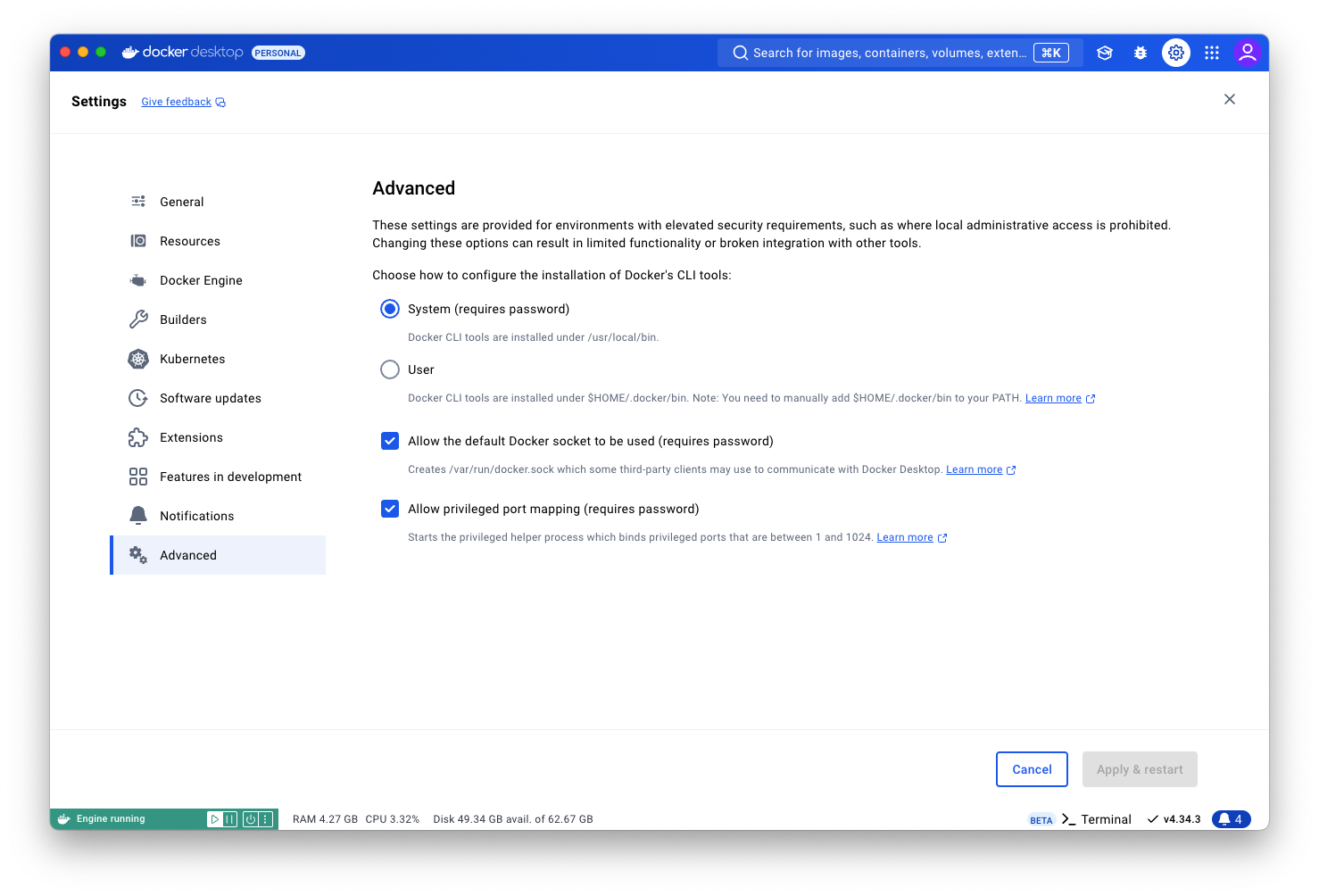
Advanced settings look differentIf your settings page looks different or some options are missing, that's fine - things should work out of the box then.
Testing Docker Desktop
To test if the installation and tweaking of Docker Desktop has been successful, spin up a terminal and run the following command:
docker run --rm -p 80:80 hello-world
The output should look like this:
docker run --rm -p 80:80 hello-world
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(arm64v8)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/